Feeling Left Out When Others Talk About Stocks and Mutual Fund?
Do conversations about the stock market make you anxious because you don’t understand them?
You constantly hear things like, “Mr. X made huge profits from Stock Y,” and feel the urge to invest too — but you’re unsure where to start or how it really works.

This post is for you!
We’ll walk you through a beginner-friendly approach to entering the stock market — starting with the absolute basics and building your confidence step by step.
Smart Ways to Invest in Stocks and Equities
- Mutual Fund
- Direct Stocks
- Derivatives
- Forex Trading
Among all the ways to invest, mutual fund are a great starting point if you’re new to the equity market and don’t have much experience.
What is a Mutual Fund?
Let’s not jump straight into investing just yet.
Think back to your childhood — when you received pocket money, what did you usually do? Most of us either kept it safely with us or handed it over to our parents or grandparents to save it on our behalf.
This simple habit reflects a basic principle: we often trust someone more experienced to handle our money wisely. Similarly, when it comes to the stock market, if we don’t have the knowledge or time to manage investments ourselves, we rely on an expert — and in the world of mutual fund, that expert is called a Fund Manager.
Mutual Fund Manager:
All mutual funds are managed by a dedicated fund manager, who makes investment decisions based on the fund’s objective and type. Depending on the fund category, the fund manager allocates money across different companies and sectors to meet the fund’s goals — a topic we’ll explore in the following sections.

By now, you might have a basic idea of what a mutual fund is — but is that all there is to know?
The short answer is: No.
There’s much more to mutual funds than just the definition. In the sections that follow, we’ll dive deeper into key concepts, types, benefits, and how mutual funds actually work.
Types of Mutual Funds
Mutual fund come in many types, classified by various factors.
But to keep things simple for beginners, we’ll break them down into the most important categories below.
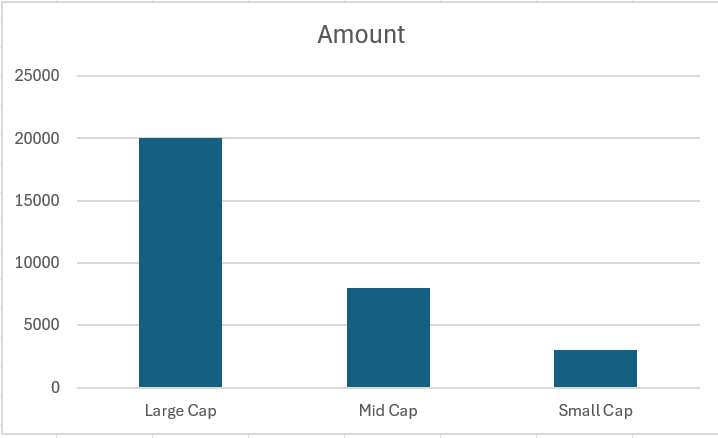
#1. Market Capitalization
In this category mutual funds are categorized based on the company capital amount.
| Company Capital | Mutual Fund Category |
| 20,000 Cr or more | Large Cap Fund |
| 5,000 Cr to 20,000 Cr | Mid Cap Fund |
| Less than 5,000 Cr | Small Cap Fund |
#2. Growth vs Dividend
When a company performs well and generates profits, it may choose to share those profits with its shareholders in the form of dividends.
Based on how these dividends are handled, mutual funds are categorized into two types: Growth and Dividend (also called Income Distribution).
Dividend Option: The profits are paid out directly to the investor at regular intervals (monthly, quarterly, or annually), depending on the fund.
Growth Option: Instead of paying dividends to the investor, the fund reinvests the profits back into the fund. This helps the investment grow over time through compounding.
when to choose what
| Growth | Dividend |
| To generate the regular income from your investment | To stay invested for long term horizon and earn compound returns |
| receive the regular payouts | The returns are higher, but in case of downfall in the market user might lose the capital invested |
#3. Based on Asset Class
Mutual funds are also classified based on the type of assets they primarily invest in.
This classification depends on where the majority of the fund’s capital is allocated.
Here are some common examples based on asset type:
| Type | What It Invests In | Risk & Return Level |
| Equity Funds | Stocks/shares | High risk, high return |
| Debt Funds | Bonds, treasury bills, fixed income | Low to medium risk |
| Hybrid Funds | Mix of equity & debt | Balanced risk/return |
| Money Market Funds | Very short-term debt instruments | Very low risk, low return |
#4. Other Specialized Funds
In this category funds are categorized based on the sector they invest and also the location-based investment. Below are the some of the examples for the same.
| Fund Type | Purpose |
| Thematic Fund | Invest in specific sector like IT, Finance and Pharma etc… |
| Fund of Funds | Invests in other mutual Funds |
| Balanced Advantage Fund | Dynamically Adjusts the equity/debt mix |
| Target Maturity Funds | Invest in bonds maturing on fixed date |
#4. Based on Maturity Period
All the above-mentioned mutual funds are categorized based on the maturity period like mentioned below.
| Type | Meaning | Best for |
| Open-Ended | We can invest/redeem at any time | Most common, flexible |
| Close-Ended | Fixed Maturity, lock-in period | Committed Investor |
| Interval Funds | Can invest/redeem at specific intervals | Less liquidity |
How to choose the Right one?
Any mutual fund can be selected based on the goal and risk ability. Let me write it down some of the common goal types with funds selected.
- Long Term Growth: Equity, ELSS and Index Funds
- Regular Income: Debt and Income Funds
- Safety & liquidity: Liquid and Money market funds
- Tax Savings Under Section 80C: ELSS (Equity Linked Savings Scheme)
- First Time Invester: Balanced/Hybrid Funds
Let me know your thoughts on this and ask if you have any questions on mutual funds.
Next Blog Preview:
We’ll explain key mutual fund concepts such as Expense Ratio, Exit Load, NAV (Net Asset Value), how mutual fund units are allotted, and the difference between Direct vs Regular (Non-Direct) Mutual Funds.
Open Demat account using:
Upstox: https://upstox.onelink.me/0H1s/2QBH4Y
Zerodha: https://zerodha.com/open-account?c=UI9061
FundsIndia: https://www.fundsindia.com/registration/signup?referrer=14c986bdd27841eabe42ce2aaa37815b




Very well written.
Also Could you please explain some of the terms used in this blog like index funds
Our Next blog will cover about the Index funds and types of Index funds along with some examples.
https://wealthy-wisdom.com/index-funds-india-2025/